Subtractive manufacturing is a critical process in the aerospace and defense industries, shaping materials into precise components essential for various applications. As procurement professionals in these sectors, it’s important to understand the different types of subtractive manufacturing to make informed decisions when sourcing components and materials. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the most common subtractive manufacturing processes.
1. CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is the cornerstone of modern subtractive manufacturing. It uses computer-controlled machines to shape a workpiece into the desired form. CNC machining is highly accurate and can produce complex geometries with tight tolerances, making it ideal for aerospace components where precision is paramount.
Types of CNC Machining:
- Milling: Involves rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. It’s versatile and can create a wide range of shapes.
- Turning: The workpiece rotates while a stationary cutting tool removes material, suitable for creating cylindrical parts.
- Drilling: Used to create precise holes in materials, an essential process in many aerospace components.
2. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM is a specialized subtractive process where material is removed from a workpiece using electrical discharges or sparks. This method is particularly useful for materials that are hard to machine with traditional methods, such as superalloys used in jet engines.
Types of EDM:
- Wire EDM: Uses a thin wire as an electrode to cut intricate and delicate shapes.
- Sink EDM: Also known as ram EDM, where a shaped electrode sinks into the workpiece to create complex cavities or shapes.
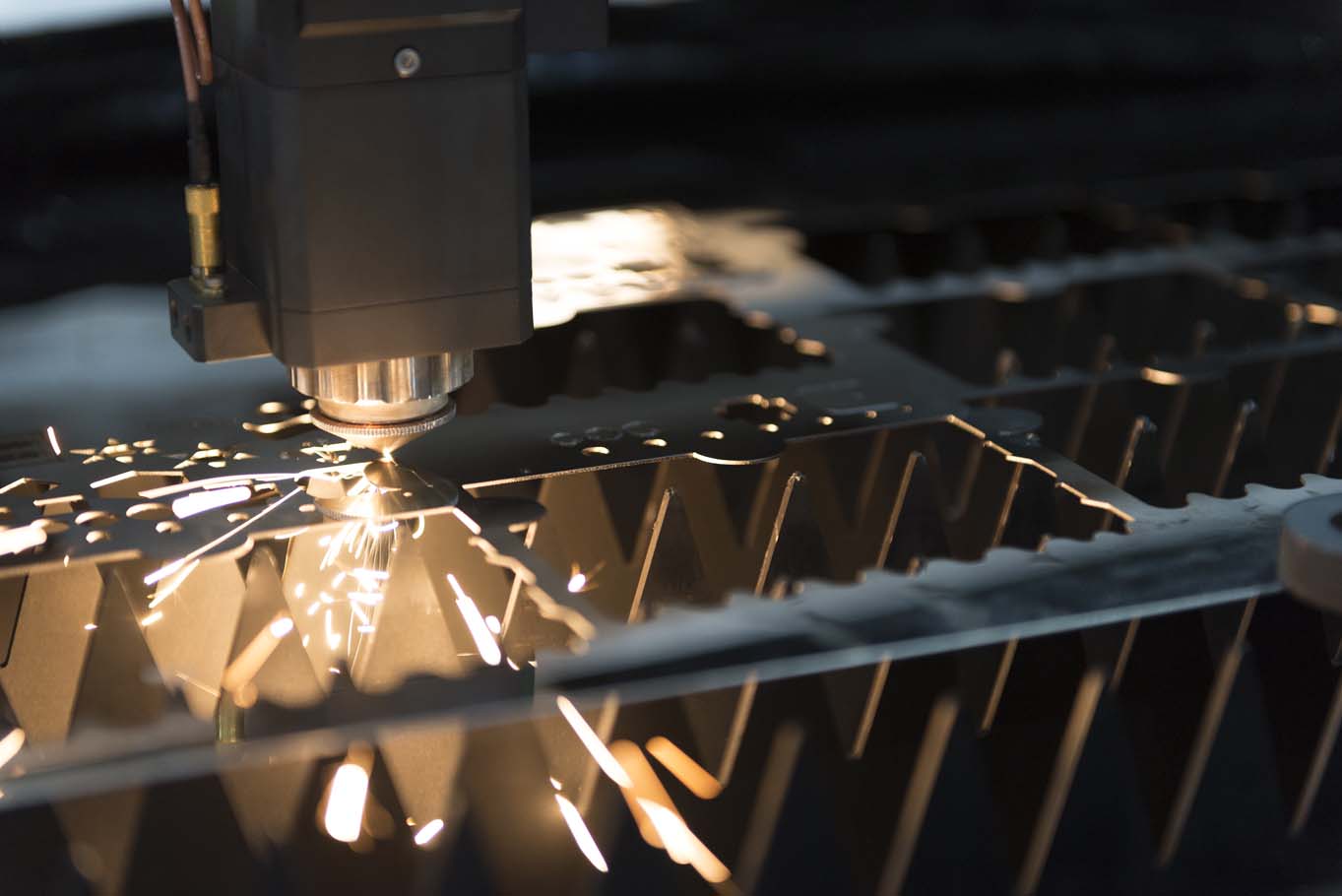
3. Laser Cutting
Laser cutting uses a high-powered laser beam to cut or engrave materials. It’s known for its precision and ability to cut complex shapes in a range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, which are commonly used in aerospace applications.
4. Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive particles, to cut materials. This method generates no heat, making it ideal for materials sensitive to high temperatures. It’s useful for cutting composites, a common material in the aerospace industry.
5. Grinding
Grinding uses an abrasive wheel to remove material from a workpiece. It’s used for finishing operations to achieve high surface quality and dimensional accuracy, essential in aerospace parts where surface finish is crucial for performance and safety.
6. Broaching
Broaching involves a multipoint cutter passing over a workpiece to remove material. It’s used to create unique shapes or keyways in parts and is notable for its ability to produce precision cuts with a smooth finish.
Benefits of Subtractive Manufacturing in Aerospace and Defense
Subtractive manufacturing offers several benefits:
- Precision: Capable of producing parts with tight tolerances, essential for aerospace applications.
- Versatility: Can handle a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
- Surface Finish: Achieves high-quality surface finishes, critical in aerospace components for aerodynamic efficiency and fatigue resistance.
Challenges and Considerations
While subtractive manufacturing is invaluable, it also presents challenges:
- Material Waste: Subtractive processes often produce significant waste material. It can usually be recycled.
- Cost: High precision and quality come at a cost, especially for complex parts.
- Machining Time: Some processes can be time-consuming, impacting production schedules.
Subtractive Manufacturing in Aerospace & Defense
For procurement professionals in the aerospace and defense industries, understanding these different subtractive manufacturing processes is key to sourcing the right components and materials for your needs. Each method offers unique benefits and is suited to particular applications, depending on the material, required precision, and complexity of the parts. Balancing these factors with cost and production time will guide you in making the most appropriate and cost-effective decisions for your projects.
Remember, the choice of manufacturing process can significantly impact the performance, durability, and cost of aerospace components. As technology evolves, staying informed about these processes ensures that you can continue to make decisions that align with industry advancements and requirements.